The chemical name for Lasix is furosemide. This potent diuretic is widely prescribed for managing fluid retention in various medical conditions.
Understanding the chemical name allows for precise identification and avoids potential confusion with similar-sounding medications. Always confirm the chemical name on your prescription to ensure you’re receiving the correct drug. This is especially important when discussing your medication with healthcare professionals or pharmacists.
Remember, furosemide (Lasix) is a powerful medication. Incorrect usage can lead to serious complications. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and inform them about any other medications you’re taking to avoid potential drug interactions. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience unexpected side effects.
For detailed information on dosages, potential side effects, and contraindications, consult your physician or refer to the official product information leaflet. Never self-medicate; proper medical guidance is paramount for safe and effective treatment.
- Lasix Chemical Name
- The IUPAC Name and Chemical Formula of Furosemide
- Chemical Formula
- Understanding the Formula
- Understanding Furosemide’s Chemical Structure and Properties
- Understanding the Sulfonamide Moiety
- Other Structural Features
- Clinical Significance of Knowing Furosemide’s Chemical Name
- Improved Communication and Precision
- Facilitating Research and Development
- Understanding Drug Metabolism and Excretion
- Regulatory Compliance and Quality Control
Lasix Chemical Name
Lasix’s chemical name is furosemide. This is a potent loop diuretic.
Furosemide’s molecular formula is C12H11ClN2O5S. This precise formula helps identify and differentiate it from other medications.
Understanding the chemical name allows for accurate identification of the drug’s composition. This is crucial for pharmacists, physicians, and researchers.
Always consult a healthcare professional for proper usage and dosage information regarding furosemide or Lasix. They can provide tailored advice based on individual needs and health conditions.
The chemical name is a cornerstone of accurate drug identification and management. Pharmacologists utilize this precise terminology for research and development.
The IUPAC Name and Chemical Formula of Furosemide
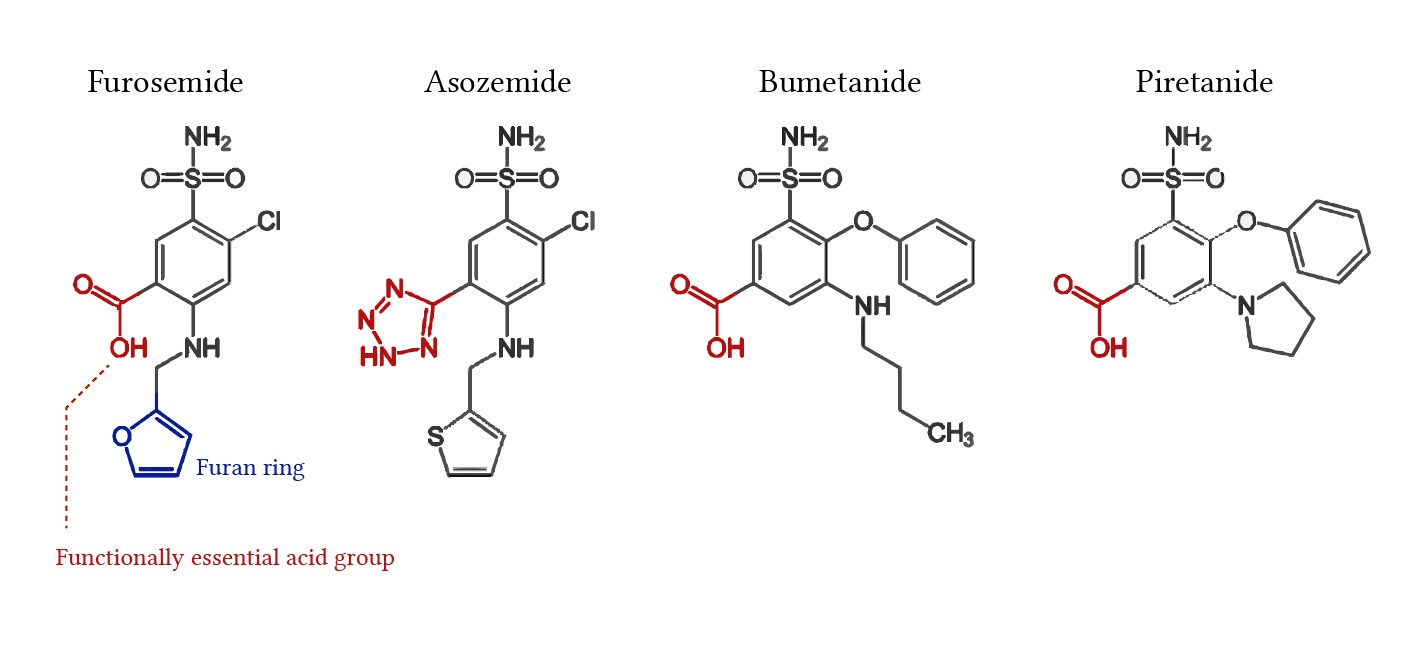
Furosemide’s IUPAC name is 4-chloro-N-furfuryl-5-sulfamoylanthranilic acid. This precisely describes its chemical structure.
Chemical Formula
Its chemical formula is C12H11ClN2O5S. This formula provides a concise representation of the elements and their respective quantities within a single molecule of furosemide.
Understanding the Formula
The formula shows that each furosemide molecule contains 12 carbon atoms (C), 11 hydrogen atoms (H), 1 chlorine atom (Cl), 2 nitrogen atoms (N), 5 oxygen atoms (O), and 1 sulfur atom (S). This information is critical for understanding its chemical properties and behavior.
Understanding Furosemide’s Chemical Structure and Properties
Furosemide, the active component in Lasix, possesses a unique chemical structure crucial to its function. Its molecular formula is C12H11ClN2O5S, reflecting its composition of carbon, hydrogen, chlorine, nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur atoms. This arrangement forms a sulfonamide derivative, specifically a loop diuretic.
Understanding the Sulfonamide Moiety
The sulfonamide group (-SO2NH2) is central to furosemide’s mechanism of action. This group interacts with the chloride binding site in the sodium-potassium-chloride co-transporter (NKCC2) in the kidney’s thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop. This interaction inhibits the reabsorption of sodium, potassium, and chloride ions, leading to increased excretion of water and electrolytes in urine.
Other Structural Features
Beyond the sulfonamide, a benzene ring and a carboxyl group contribute to furosemide’s properties. The benzene ring enhances its lipophilicity, assisting its absorption into the body. The carboxyl group (-COOH) influences its ionization and solubility at different pH levels, affecting its absorption and distribution. The chlorine atom adds to the molecule’s overall chemical stability and may influence its interactions with biological targets.
These structural features, combined, account for furosemide’s potent diuretic effects, rapid onset of action, and relatively short duration. Understanding this chemical structure allows for a deeper comprehension of its mechanism, potential drug interactions, and metabolic pathways.
Clinical Significance of Knowing Furosemide’s Chemical Name
Knowing furosemide’s chemical name, 4-chloro-N-furfuryl-5-sulfamoylanthranilic acid, offers several practical advantages for healthcare professionals and researchers.
Improved Communication and Precision
- Precisely identifying the drug prevents medication errors stemming from ambiguous names or abbreviations.
- Clear communication among pharmacists, physicians, and other healthcare providers ensures accurate prescribing and dispensing.
- This precision is especially critical in emergency situations or when dealing with patients with complex medical histories.
Facilitating Research and Development
- The chemical name allows for targeted literature searches on furosemide’s chemical properties, pharmacological interactions, and metabolic pathways.
- Researchers can easily compare furosemide to similar compounds, facilitating the development of new diuretics or related medications.
- Understanding its chemical structure helps in identifying potential drug interactions or predicting adverse effects.
Understanding Drug Metabolism and Excretion
- The chemical structure provides clues about how the body processes furosemide.
- This knowledge helps predict potential drug-drug interactions and tailor dosages for specific patient populations (e.g., those with kidney impairment).
- It aids in understanding the elimination pathways and possible accumulation in the body.
Regulatory Compliance and Quality Control
The chemical name is fundamental for regulatory submissions, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and quality control processes. It ensures the drug’s purity and consistency, protecting patient safety.