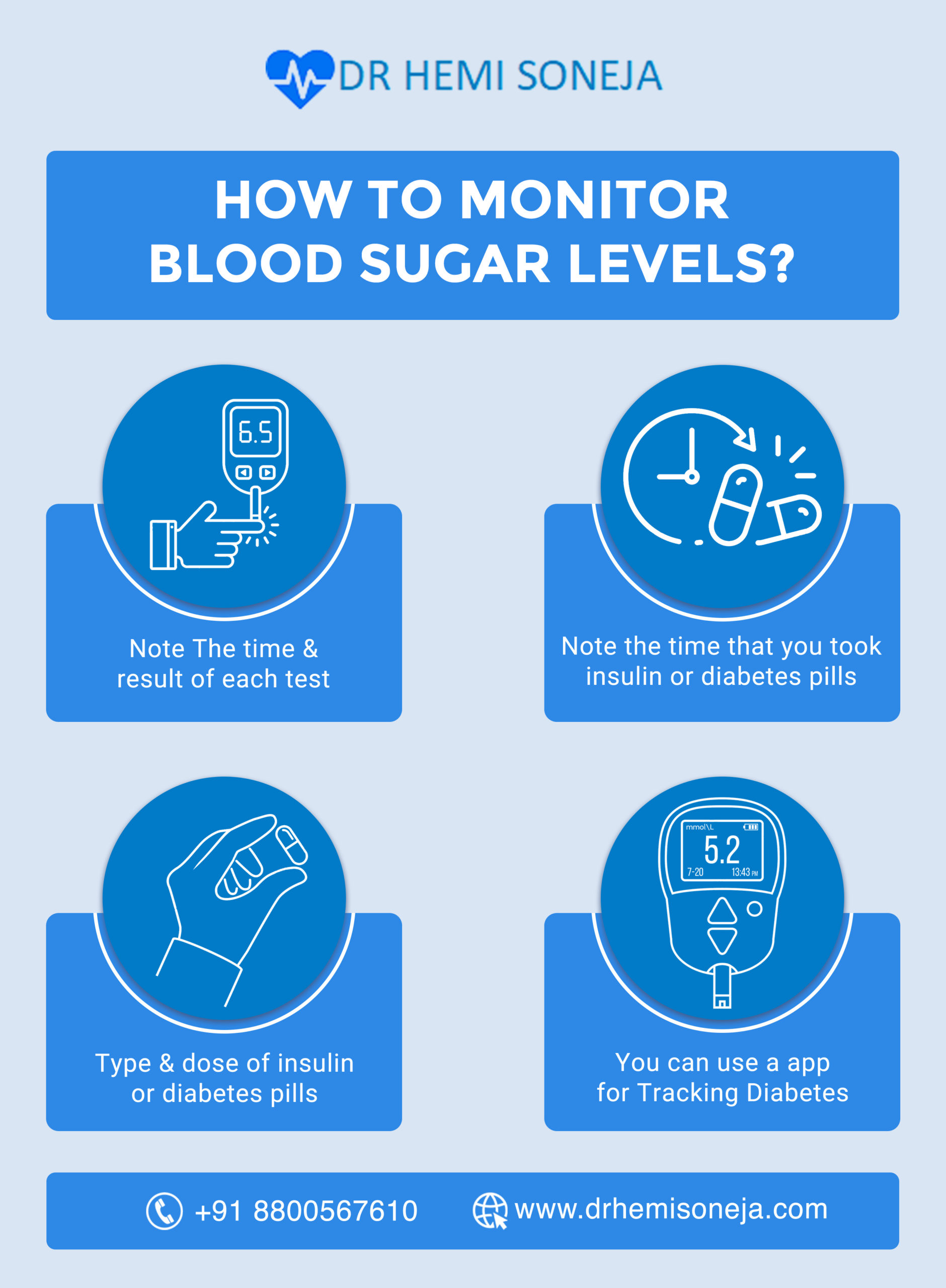
Prednisone can significantly raise your blood sugar. This is because it interferes with your body’s natural insulin production and sensitivity. If you’re prescribed prednisone, carefully monitor your blood glucose levels, especially if you have a history of diabetes or prediabetes. Regular testing is key.
Aim for glucose readings within your target range, as determined by your doctor. Consult them immediately if you notice persistently high readings. Dietary adjustments are frequently necessary. Reducing refined carbohydrates and increasing fiber intake can help stabilize blood sugar levels while taking prednisone. Consider smaller, more frequent meals instead of large ones.
Your doctor might recommend adjusting your diabetes medication, if applicable, to account for the impact of prednisone. This might involve increasing your insulin dose or switching medications. They will guide you on appropriate management strategies based on your individual needs and health status. Close communication with your healthcare provider is absolutely critical during prednisone treatment.
Remember: This information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare provider before making any changes to your medication or diet.
- Blood Glucose High with Prednisone: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Prednisone’s Effect on Blood Sugar
- Managing High Blood Glucose
- Lifestyle Adjustments for Better Control
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Understanding Prednisone’s Impact on Blood Sugar
- Recognizing the Symptoms of Prednisone-Induced Hyperglycemia
- Managing High Blood Sugar While on Prednisone
- Dietary Adjustments for Blood Sugar Control on Prednisone
- Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels and Seeking Medical Advice
- Long-Term Strategies for Managing Blood Sugar and Prednisone
Blood Glucose High with Prednisone: A Detailed Guide
Monitor your blood glucose regularly. Aim for frequent checks, especially during the first few weeks of prednisone treatment and whenever you adjust your dosage. This proactive approach helps catch spikes early.
Understanding Prednisone’s Effect on Blood Sugar
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, increases blood glucose levels by promoting gluconeogenesis (your liver producing more glucose) and reducing insulin sensitivity. This means your body uses insulin less effectively to lower blood sugar.
The degree of blood sugar elevation varies greatly among individuals. Factors influencing this include your existing health conditions, dosage, and duration of prednisone use. Higher doses and longer treatment periods generally lead to greater blood sugar increases.
Managing High Blood Glucose
Consult your doctor immediately if you experience significantly elevated blood glucose levels. They will help you develop a personalized management plan, which may involve: adjusting your prednisone dosage (if possible), adding or changing diabetes medications (like metformin or insulin), and recommending dietary changes.
Dietary modifications are vital. Focus on a balanced diet rich in fiber, lean protein, and complex carbohydrates. Limit simple sugars and processed foods. Regular exercise, such as brisk walking for 30 minutes most days of the week, plays a significant role in improving insulin sensitivity and blood glucose control.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Better Control
Maintain a healthy weight. Excess weight can worsen insulin resistance, further impacting blood sugar levels. Hydrate consistently, drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can also help regulate blood sugar.
Regular follow-up appointments with your doctor and potentially an endocrinologist are key. They will monitor your progress, make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan, and provide support. Open communication with your healthcare provider is paramount for effective blood glucose management while on prednisone.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms of hyperglycemia, including excessive thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, or slow-healing sores. Prompt action is crucial to prevent serious complications.
Understanding Prednisone’s Impact on Blood Sugar
Prednisone, a powerful corticosteroid, raises blood glucose levels by interfering with insulin’s function. It does this primarily by increasing the production of glucose by your liver and decreasing your body’s sensitivity to insulin.
This effect can be significant, especially with higher doses or prolonged use. Individuals with pre-existing diabetes are particularly vulnerable and may experience worsened glucose control. Even those without diabetes can experience elevated blood sugar levels.
Managing blood sugar while taking prednisone requires careful monitoring and often adjustments to diabetes medication, if applicable. Regular blood glucose testing, as advised by your doctor, is crucial. Your physician may recommend increasing insulin doses or adding other medications to help control your blood sugar.
| Action | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Regular blood glucose monitoring | Provides data for effective management |
| Dietary adjustments (reducing refined carbs & sugars) | Minimizes glucose spikes |
| Increased physical activity (as tolerated) | Improves insulin sensitivity |
| Close communication with your doctor | Allows for timely medication adjustments |
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, complements medical management. Closely following your doctor’s recommendations and reporting any concerning symptoms are key to minimizing the impact of prednisone on your blood sugar levels.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Prednisone-Induced Hyperglycemia
Pay close attention to your body. Prednisone can raise your blood sugar, and recognizing the symptoms early is key to managing it.
Increased thirst and frequent urination are common early indicators. You might find yourself needing to drink more fluids than usual and visiting the restroom more often. These symptoms stem from your body trying to flush out excess glucose.
- Increased Hunger: Even after eating, you might feel persistently hungry due to your body’s inability to properly utilize the glucose.
- Blurry Vision: High blood sugar can affect the lens of your eye, leading to temporary blurry vision.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Your body isn’t getting the energy it needs, resulting in feeling unusually tired and weak.
- Slow-Healing Wounds: High blood sugar impairs the body’s ability to repair damaged tissue.
- Frequent Infections: High blood sugar weakens your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections.
Less common but still possible symptoms include numbness or tingling in your hands or feet, and unexplained weight loss.
If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately. Regular blood glucose monitoring, as advised by your healthcare provider, is vital for managing prednisone-induced hyperglycemia.
- Regular Blood Glucose Monitoring: This allows for early detection and adjustment of your treatment plan.
- Dietary Adjustments: Your doctor might recommend a diet lower in carbohydrates and sugars.
- Medication Adjustments: Your doctor might adjust your prednisone dosage or prescribe additional medications to help manage your blood sugar.
Proactive monitoring and communication with your healthcare provider are crucial for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels while taking prednisone.
Managing High Blood Sugar While on Prednisone
Monitor your blood sugar regularly. Aim for testing at least twice daily, or more frequently as advised by your doctor. This allows you to track changes and adjust your management plan accordingly.
Maintain a healthy diet. Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of non-starchy vegetables. Limit sugary drinks and processed foods. Small, frequent meals can help prevent blood sugar spikes.
Increase your physical activity. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. This helps your body use insulin more effectively.
Consult your doctor about medication. They may recommend adjustments to your existing diabetes medication or prescribe additional medication to manage your blood sugar levels while on prednisone. This is crucial for preventing complications.
Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help your kidneys process glucose efficiently.
Work closely with your healthcare team. Regular checkups and open communication are key. They can provide personalized guidance and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
Consider working with a registered dietitian or certified diabetes educator. They can provide tailored dietary advice and support.
Note: This information is for general knowledge and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional for any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment.
Dietary Adjustments for Blood Sugar Control on Prednisone
Prioritize low-glycemic index (GI) foods. These foods release glucose slowly into your bloodstream, preventing spikes. Think whole grains like brown rice and quinoa, most vegetables, and legumes.
Increase your fiber intake. Fiber slows digestion and glucose absorption. Good sources include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Aim for at least 25-30 grams daily.
Choose lean protein sources. Protein helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes satiety, preventing overeating. Include chicken breast, fish, beans, and lentils in your diet.
Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbohydrates. These contribute significantly to blood sugar fluctuations. Cut down on white bread, pastries, and sugary sodas.
Control portion sizes. Even healthy foods can raise blood sugar if consumed in excess. Use smaller plates and be mindful of serving sizes.
Spread your carbohydrate intake throughout the day. Avoid large carbohydrate meals, instead opting for smaller, more frequent meals. This prevents large blood sugar spikes.
Consult a registered dietitian or certified diabetes educator. They can create a personalized meal plan that suits your specific needs and health conditions.
Monitor your blood glucose regularly. This allows you to track your progress and adjust your diet as needed. Keep a food diary to help identify patterns and triggers.
Stay hydrated. Drinking plenty of water helps regulate blood sugar and overall health.
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels and Seeking Medical Advice
Check your blood glucose regularly, ideally before meals and before bed. Use a reliable glucose meter and record your readings in a logbook or app. Consistent tracking helps you and your doctor identify patterns.
Target glucose levels vary depending on individual circumstances and should be discussed with your physician. They will provide personalized recommendations, taking into account other health conditions.
Report any unusually high or low readings immediately to your doctor. Don’t hesitate to contact them if you experience symptoms like excessive thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, or unexplained fatigue.
Discuss your medication regimen with your doctor. They may adjust your prednisone dosage or prescribe additional medications, like metformin or insulin, to manage blood glucose levels. Regular follow-up appointments are vital for ongoing monitoring and treatment adjustments.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle. Eat a balanced diet, focusing on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Incorporate regular physical activity into your daily routine. These lifestyle changes significantly impact blood sugar control.
Learn about potential side effects of prednisone and how to recognize them. This empowers you to better manage your health and communicate effectively with your healthcare provider.
Consider working with a registered dietitian or certified diabetes educator for personalized guidance on nutrition and lifestyle modifications tailored to your needs.
Long-Term Strategies for Managing Blood Sugar and Prednisone
Maintain a consistent, healthy diet. Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of non-starchy vegetables. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbohydrates. Regular blood glucose monitoring provides crucial data for adjustments.
Regular exercise is key. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity weekly. Strength training twice a week further improves insulin sensitivity. Consult your doctor before starting any new exercise program.
Work closely with your doctor and diabetes educator. They can help you create a personalized plan, including medication adjustments and lifestyle recommendations. Regular check-ups are necessary for monitoring your progress.
Consider medication adjustments. Your doctor might prescribe medications to help manage your blood sugar, such as metformin or insulin. They may also adjust your prednisone dose if possible to minimize its impact on your blood glucose levels.
Prioritize stress management. High stress levels can raise blood sugar. Incorporate relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises into your daily routine. Adequate sleep is also vital.
Track your blood sugar levels diligently. This allows you to identify patterns and make necessary changes to your diet, exercise, or medication. Keep a detailed log to share with your healthcare provider.
Understand your medication side effects. Be aware of how prednisone and other medications affect your blood sugar. This knowledge allows for proactive adjustments and better management of your condition. Discuss any concerns with your physician immediately.